Introduction
VPS performance should be measured, not assumed. Whether you run trading platforms, automated strategies, or always-on applications, understanding how your VPS actually performs helps you identify bottlenecks, verify provider claims, and maintain system stability.
This guide explains exact steps how to check VPS performance, including CPU, memory, disk, network latency, uptime, and benchmark score testing — using practical tools and repeatable methods.
1. Prepare Your VPS for Accurate Testing
Before running any performance tests:
- Log in to your VPS via Remote Desktop (Windows)
- Close unnecessary applications and background tasks
- Ensure no platform updates or maintenance tasks are running
- Run tests during normal workload hours, not just idle time
- Note your VPS location (e.g., Chicago)
⚠️ Performance tests should reflect real usage conditions, not best-case scenarios.
2. How to Test CPU Performance on a VPS
CPU performance is one of the most important factors in overall VPS responsiveness — especially for trading platforms, real-time charting, and automated strategies.
In this section, we’ll cover two reliable ways to evaluate CPU performance on a Windows-based VPS.
Method A: Basic CPU Monitoring (Windows)
- Open Task Manager
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc, or
- Right-click the taskbar → Task Manager
- Navigate to CPU Performance
- Click Performance
- Select CPU
- Observe Key CPU Metrics
Pay attention to the following indicators:- Base speed vs current speed
→ Confirms whether the CPU is running at expected frequencies. - Utilization during workload
→ Watch how usage changes when platforms, charts, or strategies are active. - Frequency stability
→ Observe whether clock speed remains stable or fluctuates frequently.
- Base speed vs current speed
What to look for:
- Stable clock speeds under sustained load
- No frequent drops caused by throttling
- Smooth responsiveness when running multiple tasks or platforms simultaneously
⚠️ Warning:
If clock speeds drop sharply while CPU usage is high, it may indicate:
- CPU throttling
- Oversubscription
- Power or thermal limitations
This is common with low-quality or heavily shared VPS environments.
Method B: CPU Benchmark Test (Recommended)
Basic monitoring shows behavior, but benchmark testing provides measurable performance data.
Benchmark tests help you evaluate:
- Raw CPU processing capability
- Single-thread responsiveness
- Multi-thread consistency
- Effects of CPU oversubscription
For trading VPS environments, consistent single-thread performance matters more than peak multi-core scores.
Step 1: Download Passmark Performance Test Tool
PassMark is a widely used, industry-recognized benchmarking tool.
Visit : ➡ https://www.passmark.com/products/performancetest/download.php
- Download the Windows version
- Most trading VPS environments run Windows Server, which is fully supported
Step 2: Install the software
- Double-click the installer
- Click Next through the setup steps
- Complete installation
No advanced technical knowledge is required.
Step 3: Run the Full Benchmark
- Open PerformanceTest
- Click “Run Benchmark” or “Run All Tests”
PassMark will automatically test:
- CPU arithmetic performance
- Compression and decompression
- Encryption workloads
- Memory latency
- Disk read/write speed
- Basic graphics rendering
⏱️ The full test typically takes about 5 minutes.
During the test, avoid running other applications for accurate results.
Step 4: Check Your CPU Mark Score
After completion, note your CPU Mark score.
This is the single most important benchmark number for evaluating VPS CPU performance.
In real trading environments, a higher CPU Mark generally means:
- Faster indicator calculations
- Smoother chart updates
- More responsive platforms
- Better performance for automated strategies
Step 5: Compare Your Results with Real Hardware
PassMark allows you to compare your VPS performance against:
- Modern desktop CPUs
- Enterprise server CPUs
- Other VPS environments
- Historical benchmark data
This comparison helps you understand whether your VPS performs like:
- A modern high-performance Ryzen system, or
- An outdated, oversold CPU often found in low-quality hosting
This step is critical for separating real performance from marketing claims.
Example: TradoxVPS CPU Benchmark Transparency
To provide transparency, TradoxVPS publishes real benchmark scores for each VPS tier:
TradoxVPS Starter Trader VPS Plan’s Passmark Score
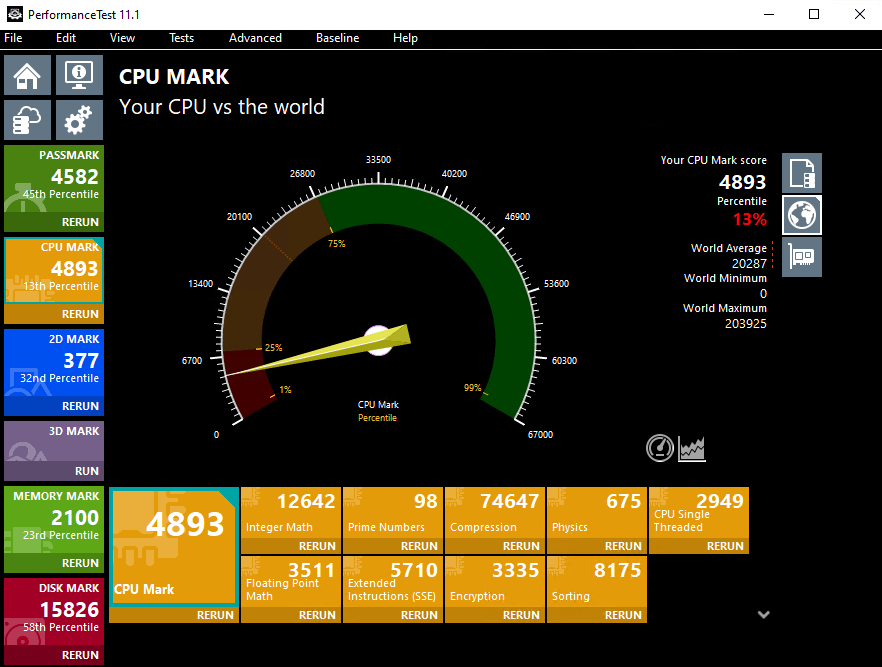
TradoxVPS Active Trader VPS Plan’s Passmark Score
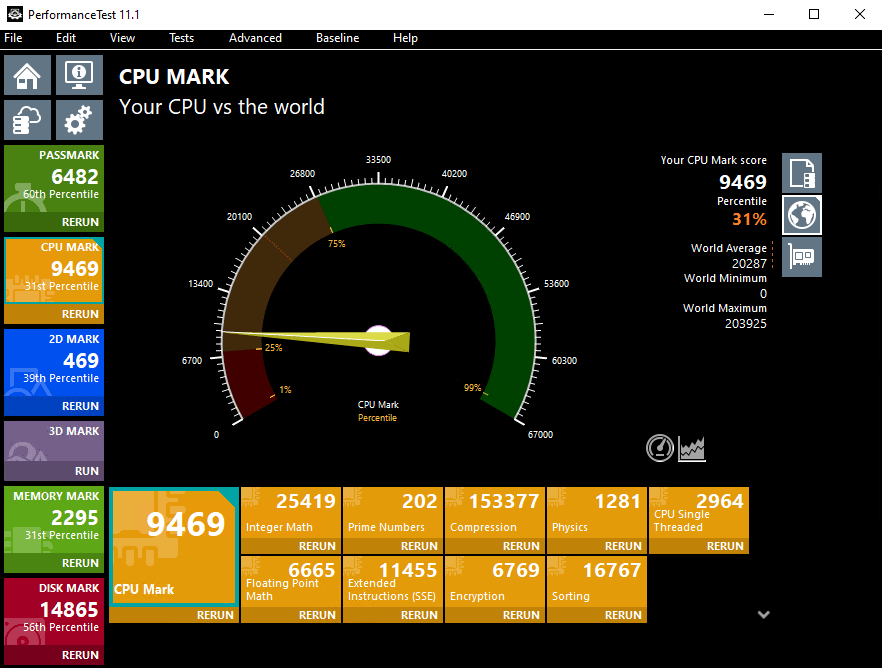
TradoxVPS Advanced Trader VPS Plan’s Passmark Score
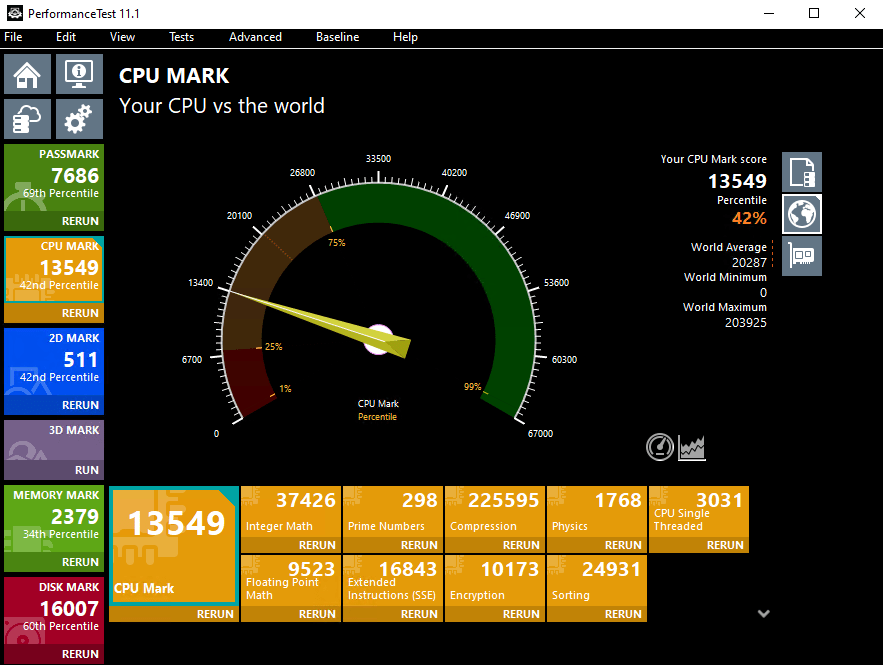
TradoxVPS High Performance VPS Plan’s Passmark Score
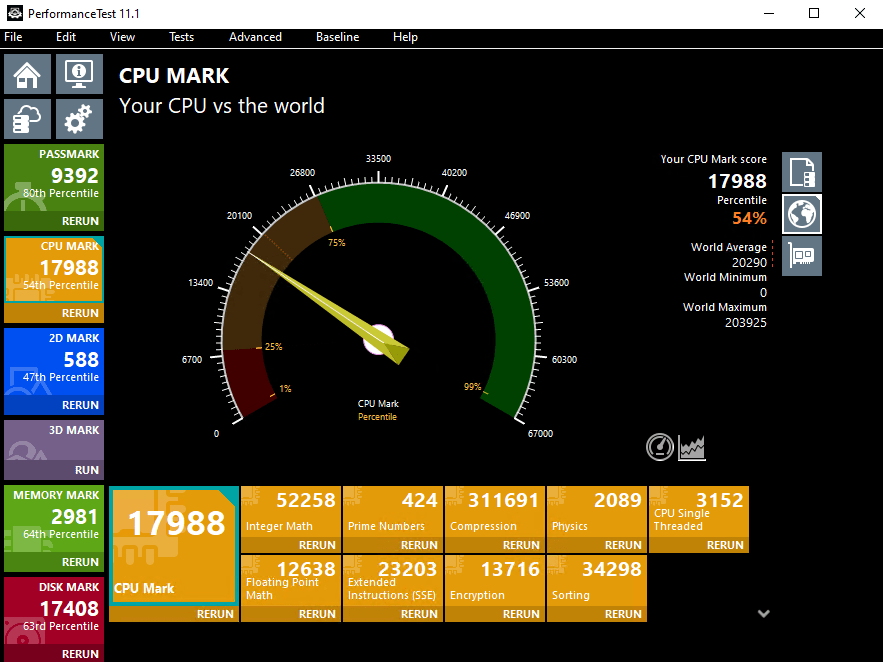
TradoxVPS Ultra Low Latency VPS Plan’s Passmark Score
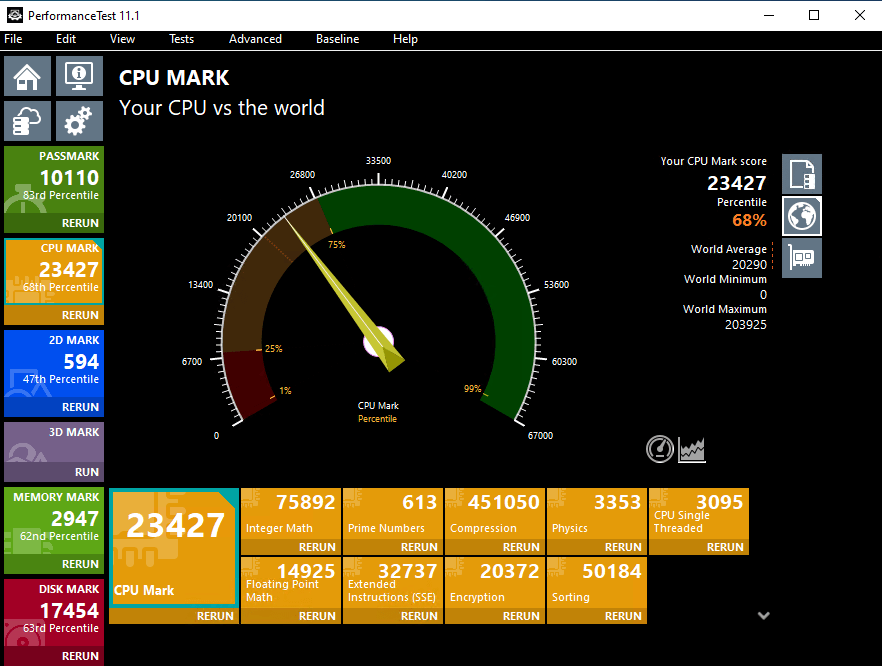
TradoxVPS Max Performance VPS Plan’s Passmark Score
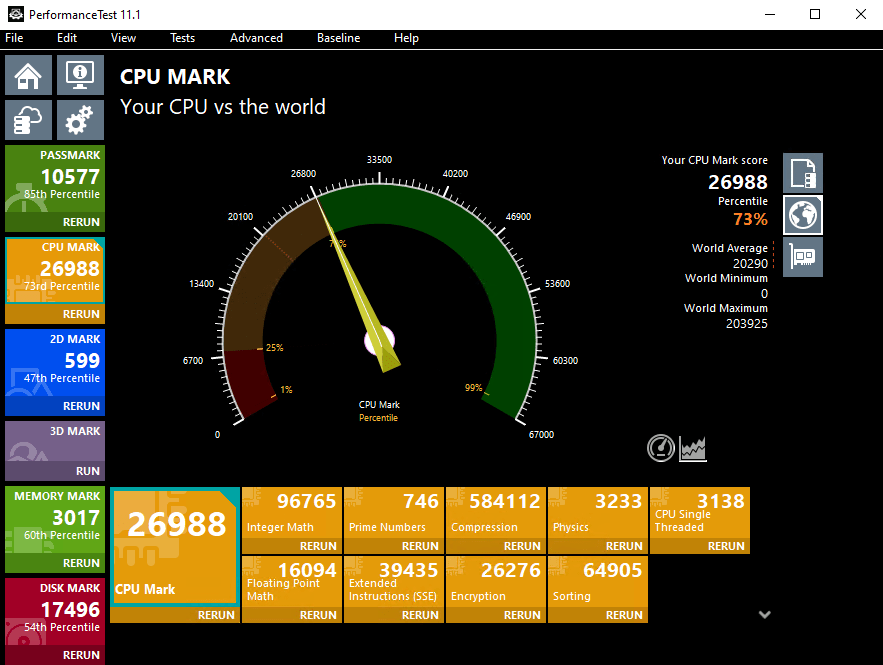
These benchmarks allow users to evaluate CPU performance before deployment, supporting informed decision-making.
3. How to Check VPS Memory Performance
Basic Memory Check
- Open Task Manager → Performance → Memory
- Review:
- Total available RAM
- Memory in use
- Cached vs free memory
What to look for:
- Enough headroom for peak workloads
- No constant memory pressure
- Smooth application switching
Advanced Memory Validation
You should confirm:
- Memory type (DDR4 vs DDR5)
- No excessive swapping or paging
- Stable performance during multi-platform usage
Memory bottlenecks often cause freezes, not crashes.
4. How to Test VPS Disk Performance (NVMe vs SSD)
Disk performance directly affects:
- Platform startup time
- Log file access
- Historical data loading
Disk Speed Test (Windows)
Recommended metrics:
- Sequential read/write speed
- Random I/O performance
- Consistency under load
Expected results:
- NVMe SSDs show significantly lower latency
- Stable throughput without sudden drops
If disk performance fluctuates heavily, it may indicate shared or oversold storage.
5. How to Check VPS Network Latency
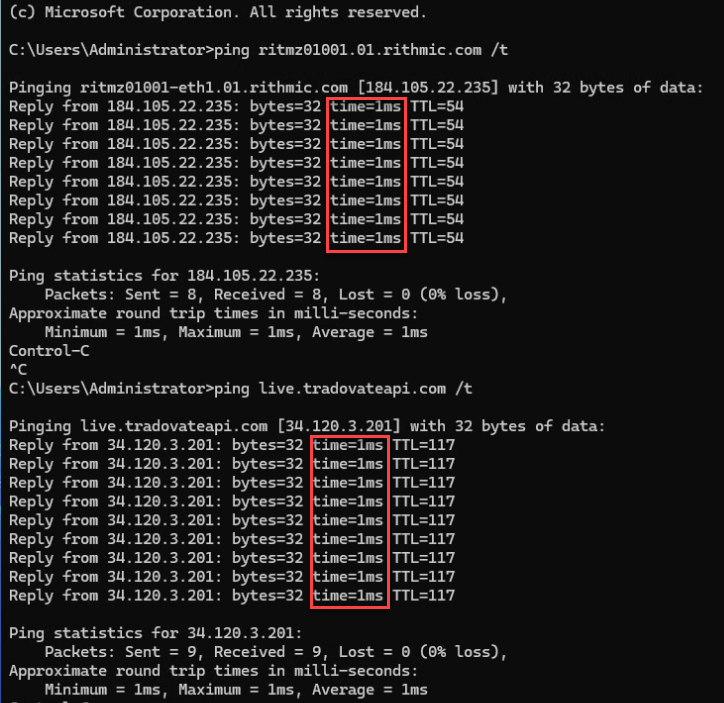
Basic Latency Test (Ping)
- Open Command Prompt
- Run latency tests to your target service (broker, exchange endpoint, etc.)
- Observe:
- Average latency (ms)
- Packet loss
- Latency spikes
Extended Network Stability Test
Run tests over:
- Different times of day
- Peak market hours
- High-volatility periods
What matters most:
- Consistency, not just low averages
- Minimal jitter
- No packet loss
For futures trading, Chicago-hosted VPS environments typically provide the most stable routes to CME infrastructure.
Chicago VPS Latency Check Results
6. Upload & Download Speed Test (Application-Based)
Upload and download speed testing helps confirm that your VPS network is not bandwidth-limited and performs consistently.
For high-performance VPS environments, application-based testing is more accurate than browser tests, especially when speeds exceed 1 Gbps.
Browser-based tests often fail to fully utilize fast VPS networks. That’s why we recommend using the Ookla Speedtest application.
Step 1: Install the Speedtest App
Inside your VPS:
- Go to: https://www.speedtest.net/apps
- Download the Windows application
- Install using default settings
This works on Windows Server VPS environments.
Step 2: Run the Speed Test
- Open the Speedtest app
- Select a nearby, high-capacity test server
- Click Go
- Let the test complete fully
Run the test 2–3 times to confirm consistency.
Step 3: Check Your Results
Note the following values:
- Download speed
- Upload speed
- Ping
- Jitter (if shown)
For a professional VPS, speeds should be stable with no sudden drops.
Example: TradoxVPS Speed Test Results
To maintain transparency, TradoxVPS publishes real speed test results measured using the Ookla application.
7. How to Run VPS Benchmark Tests Properly
Benchmark tests provide a reference score to compare performance over time or against expected standards.
What a Benchmark Test Measures:
- CPU processing power
- Memory bandwidth
- Disk I/O performance
- System responsiveness
How to Use Benchmark Scores Correctly:
- Run benchmarks at least twice
- Compare results over days/weeks
- Avoid comparing different locations unfairly
- Use benchmarks as trend indicators, not absolute truth
A stable benchmark score over time is more valuable than a high one-time result.
8. How to Verify VPS Uptime
Uptime is critical for trading and automated systems.
You should monitor:
- Unexpected reboots
- Network interruptions
- Platform disconnects
Reliable VPS providers publish:
- Uptime statistics
- Incident history
- Maintenance notices
Without transparency, uptime claims cannot be verified.
9. How TradoxVPS Supports Performance Transparency
TradoxVPS provides:
- Benchmark performance scores
- Hardware specifications
- Latency check results
- Uptime and reliability data
This enables users to verify performance independently.
Conclusion
Checking VPS performance correctly means understanding how CPU, memory, disk, network, and uptime work together. For professional workloads, consistency beats peak performance every time.
A well-built VPS environment should provide both strong performance and the data needed to validate it.



